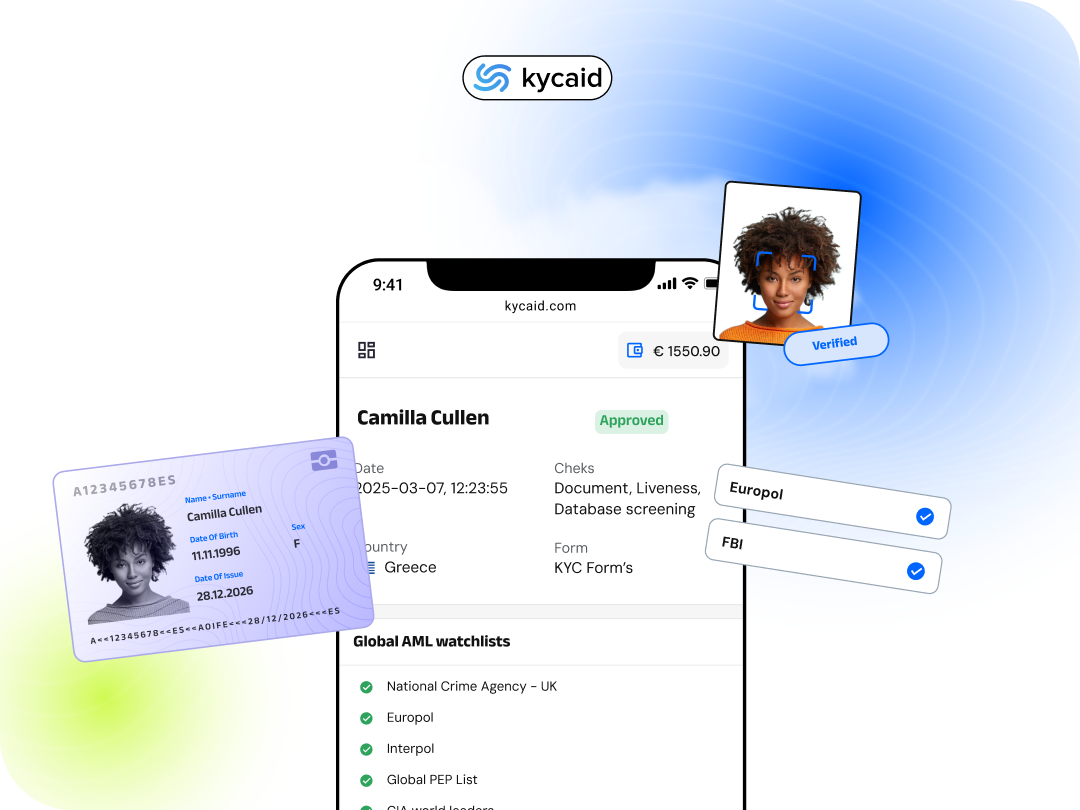
Regulations compliance, customer satisfaction, and fraud prevention all depend on remote consumer verification. Digital remote consumer verification guarantees authenticity without personal interaction. Using official records, biometrics, and database checks, the system confirms personal information. An important component of this process is secure customer onboarding, which guarantees that client IDs are checked safely right from the beginning of their path.
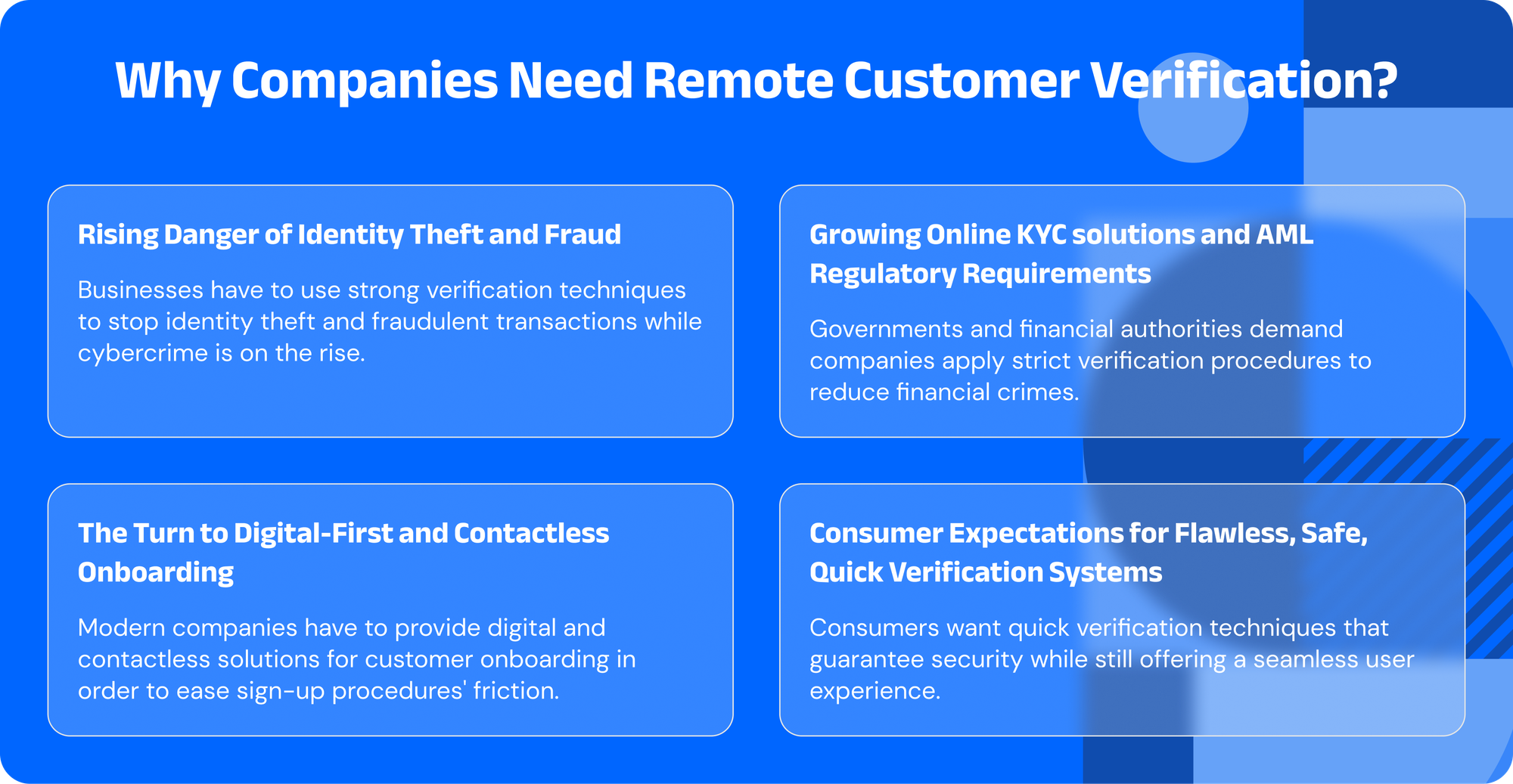
Compliance and security rely on remotely verifying customer identities when online transactions and digital services rule. It helps companies eradicate dishonesty and establish client confidence.
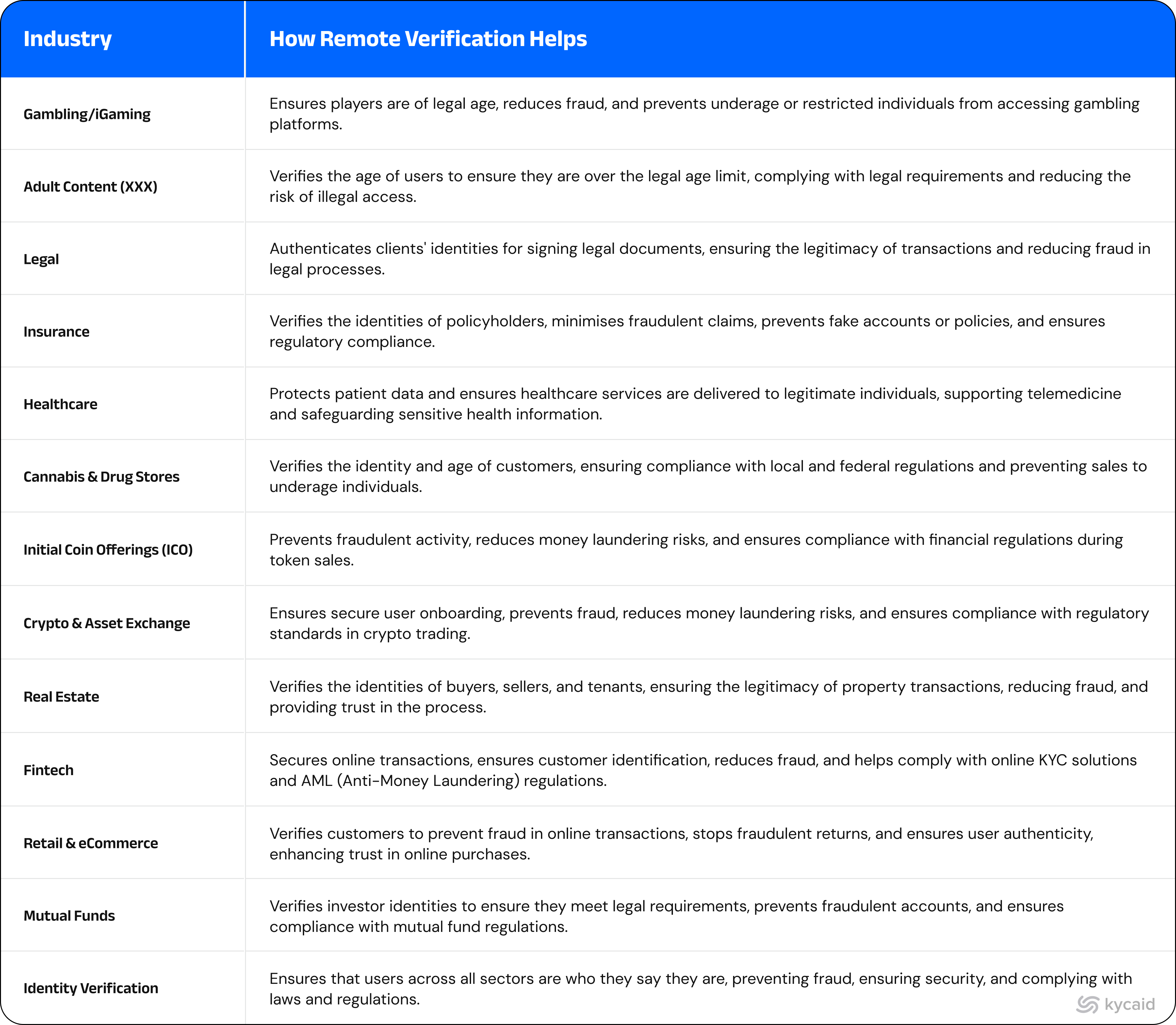
Important Sectors Profiting from Digital Identity Verification
Remote customer verification is relied upon in many different sectors, including:
General Review of Worldwide Policies Affecting Digital Identity Verification
Though rules vary across regions, important frameworks include:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) (EU): Safeguards consumer privacy.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Directives (EU, UK, US): Enforces strict KYC policies.
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF): Sets worldwide AML compliance standards.
- Know Your Customer (KYC) Rules: Followed by financial authorities globally.
Fundamental Components of Remote Customer Validation
Process for Document Verification
Usually, basic records needed for remote validation consist of:
- Government ID
- Passport
- Driver's Licence
- Permanent Residence Permit
- Domestic Passport
Tool for Automated Document Verification
AI-powered systems evaluate document authenticity by:
- Cross-referencing data with government databases
- Spotting false elements
- Verifying watermark validity
This system lowers human error and improves efficiency.
Techniques in Biometric Verification
Liveness detection guarantees that the individual under verification is physically present rather than relying solely on a stationary image. Facial recognition improves identity verification by matching a user's selfie to their official ID picture.
AI Combating Spoofing and Deepfake Fraud
Advanced artificial intelligence systems increase security by spotting bogus attempts—including deepfake videos and face masks—that might try to evade identity verification. Remote verification systems compare consumer credentials with current records, validating them against worldwide databases.
Database screening for Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) and Compliance with AML Rules
Compliance with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) rules requires businesses to screen consumers against sanctions lists and identify any politically exposed persons (PEPs), thus addressing political exposure.
Improved Security with OTP and 2FA
2FA requires an extra verification step—a one-time password (OTP) delivered via email or SMS—ensuring only permitted access, thereby improving security.
Risk Assessments and AI-Based Fraud Detection
AI-based risk assessments monitor user conduct to find behavioural abnormalities, helping identify suspicious activities intended to stop fraud.
Verifying Privacy Compliance and Data Protection
Remote verification systems must follow data protection rules, ensuring client data is safe and managed with privacy in mind.
Advantages of Real-Time Verification
Real-time verification, made possible by biometric techniques and AI-powered solutions, streamlines the process and enhances customer experience and operational effectiveness.
Methodical Guide for Online Customer Verification
First Step: Gathering Consumer Data
Businesses can gather necessary information about the applicant to begin the identity verification process. This may include:
- Government-issued document (passport, driver’s licence, etc.)
- Residential address
- Contact details, such as email address and phone number
- Liveness check data for biometric verification
- Screening information from global databases for compliance and risk assessment
Guaranteeing User-Friendly Structure Design for Optimal Conversion Rates
Well-designed forms lower desertion and raise conversion rates. Effective practices include:
- Automating input with dropdown menus and autofill
- Clearly stating directions and offering samples
- Reducing necessary fields in relation to necessary knowledge
- Guaranteeing mobile responsiveness for easy access
- Image auto-capturing
Second Step: Document Submission
Consumers should send official identity documentation in accepted forms like JPEG or PNG.
- Digital scans straight uploaded from a PC or mobile device or live photographs
Third Step: OCR and Artificial Intelligence Identity Proofing
How OCR Extracts and Verifies Data?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) cross-verified against user input, OCR technology scans documents to extract text, including names, dates, and numbers.
Locating Forged or Tampered Documents
Algorithms driven by artificial intelligence evaluate:
- Font and document layout inconsistencies
- Indices of image manipulation
- Modifications in document metadata
Fourth Step: Biometric Face Match and Liveness Detector
Checking Consumers with AI-Based Facial Recognition
To verify authenticity, facial recognition technology matches a user's selfie with their identity paperwork.
Stopping Synthetic Identity Crime and Deepfake
Liveness detection forces users to blink or move their head during verification, therefore preventing fraud.
Step Five: Global Database Cross-Checking
Guaranteeing Compliance with PEP Lists, OFAC, and AML Lists
Remote verification systems cross-reference consumer data against:
- Sanctions lists (OFAC, UN, EU, UK HMT)
- PEP databases (covering government officials and their associates)
- Wanted lists ( sought by authorities for criminal activity)
- Debtors (Individuals with unpaid debts or insolvency proceedings)
- Self-restricted ( voluntarily excluded from certain activities or markets)
The Sixth Step: Risk Scoring and Manual Review—Should It Be Necessary?
The Mechanism of Risk Assessments
Risk models driven by artificial intelligence analyse:
- Location of the client and IP address
- Behavioral tendencies and past transaction records
When Manual Intervention Calls for It
High-risk cases are manually reviewed when:
- Document authenticity is unknown.
- Global databases highlight a customer.
Step Seven: Approval, Rejection, or Additional Checking
Automating Low-Risk Client Approval
AI algorithms automatically approve low-risk candidates, therefore simplifying secure customer onboarding.
Seeking Extra Documentation If Needed
When differences show up, companies could ask for confirmation of address or secondary ID paperwork.
Step Eight: Data Security and Customer Onboarding
Adhering to GDPR and Data Protection Regulations
Companies have to follow:
- GDPR concepts of general data protection
- Policies on safe data keeping and processing
Top Guidelines for Access Control and Safe Storage
Security policies consist of:
- Sensitive data end-to-end encryption
- Role-based access limits employee access

Best Practices for Safe and Successful Remote Verification
- Use Artificial Intelligence to Improve Fraud Detection
Leverage artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance fraud detection via machine learning, which evolves over time to meet changing risks. By analysing large amounts of data, AI can identify trends that traditional methods might overlook, reducing false positives and improving the accuracy of fraud detection.
- Provide Global Accessibility and Multilingual Support
Offering verification in multiple languages ensures greater inclusivity and global accessibility. This is essential for businesses operating in diverse regions, as customers may speak different languages and need confirmation in their mother tongue for optimal clarity and ease of use.
- Optimise the Verification System Across Devices
Ensure a seamless experience across both desktop and mobile platforms to improve consumer adoption and satisfaction. Whether users are on desktops, tablets, or mobile phones, providing a smooth authentication process across all devices boosts user confidence, enhances accessibility, and encourages faster adoption while reducing drop-off rates.
- Guarantee Continuous Monitoring and Updates
Regular updates and monitoring provide flexibility, helping to maintain a secure system by adapting to new fraud tactics. This ensures businesses stay ahead of potential risks as fraud methods evolve, preserving a high level of security and ensuring compliance with changing regulations.
- Use Risk-Based Verification for Effectiveness
Not every customer carries the same level of risk. A risk-based verification strategy allows businesses to dynamically adjust the verification process based on the assessed risk of each transaction. This approach ensures a smoother user experience for low-risk customers while implementing more stringent checks for higher-risk transactions.
Why Choose KYCAID for Online Verification?
- Fast & Secure Onboarding: Seamless identity verification that enhances the customer experience and reduces wait times.
- AI-Powered Fraud Detection: Advanced algorithms that improve accuracy and minimise false positives.
- Effortless Integration: APIs that integrate easily with existing systems, ensuring minimal disruption.
- Scalable Compliance Solutions: Flexible pricing tailored to your business size and needs:
- Startups & SMEs: Affordable, scalable solutions to stay compliant.
- Large Corporations: Customised packages designed to meet complex requirements.
- Global Coverage & Compliance: Serving 200+ countries, ensuring compliance with GDPR, AML, and local regulations.
- Enhanced Security: Biometric authentication and real-time monitoring for quick response to suspicious activity.
In the digital age, businesses rely on remote identity verification to ensure compliance with international regulations. This not only enhances security but also boosts client trust.